Meiji Era
The Meiji era brought a new urban model, inspired by the West Paved roads, brick buildings and gas street lights all emerged On this new model, the Westerninspired architecture of Ginza and Marunouchi districts emerging The Tokyo station, although completed in 1914, is also of European inspiration, with its red brick facade.

Meiji era. The Meiji era (明治, Meiji, Japanese pronunciation meꜜː(d)ʑi) is an era of Japanese history which extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912 This era represents the first half of the Empire of Japan, during which period the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonisation by European powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialised nation. Events of the Meiji period The years in which Meiji was the Japanese monarch comprise this modern period or era 1868 (Meiji 1) Meiji Restoration;. Chinese ·Meiji era of Japanese history 明治憲法 / 明治宪法 ― míngzhì xiànfǎ ― the Meiji Constitution··(historical) The Meiji era the Japanese era beginning in 1868 and ending in 1912 明治(めいじ)二年(にねん) Meiji ni nen the second year of Meiji (1869 in the Gregorian calendar).
Emperor Meiji died in 1912 ending the Meiji Period and moving Japan toward a new time period In 19, eight years after the emperor's death and six years after his wife died, a Shinto shrine was constructed for their souls Meiji Jingu (pictured at left) is located in Harajuku section of Tokyo. The Meiji period, which ran from 1868 to 1912, marks one of the key turning points in both Japanese architecture and the history of the country as a whole The almost 300yearlong Edo era ended abruptly in 1868 when Emperor Meiji took over in a bid to bring Japan up to speed with the Western world. The Meiji Period began with a political revolution that brought about the fall of the Tokugawa shogunate and returned the nation to the direct rule of the emperor Meiji The leaders of the Meiji Restoration were primarily young samurai who were concerned by growing domestic problems and realized that in order to escape the threat of foreign encroachment, Japan must emerge from feudalism and.
Meiji Period (1868 – 1912) With the collapse of the Tokugawa shogunate and the final defeat of Tokugawa loyalists in the Boshin War (1868 – 1869), the Emperor Meiji was restored to direct suzerainty and the imperial court (and national capital) was moved to Edo, renamed Tōkyō (“Eastern Capital”). The Meiji era brought a new urban model, inspired by the West Paved roads, brick buildings and gas street lights all emerged On this new model, the Westerninspired architecture of Ginza and Marunouchi districts emerging The Tokyo station, although completed in 1914, is also of European inspiration, with its red brick facade. Secondly, the Meiji government was founded and Japanese Westernization began This era was named Postwar Japan These changes took place because of the 3,000 foreign experts in a variety of specialist fields The foreign experts transformed English, science, engineering, army, and the navy.
The Meiji Period was a time of innovation and change in Japan It started in 1868 and ended in 1912 and received its name from Emperor Meiji The previous isolation enforced by Japanese rulers. Era name changed to Meiji 1869 New government wins total control of Japan as Boshin Civil War ends Domains return territory and citizens to the state 1871 Domains replaced by prefectures. The Meiji period or Meiji era extended from the 23rd of October 1868 to the 30th of July in 1912 This was the period that represented the first half of Japan’s empire The Japanese society shifted from being a remote feudal society to a Westernized form.
The Meiji period () was an era of dynamic political, economic, and social change that paved the way for the modernization of Japan The medical organization in the Japanese Army and the activity of army pharmacists during the Meiji period () are described. The era began 1867 to a date in Meiji 1911 to a date in Taisho 1925 to a date in Showa 19 to a date in Heisei Meiji 1 = 1868 Meiji 2 = 1869 Meiji 3 = 1870 Meiji 4 = 1871 Meiji 5 = 1872 Meiji 6 = 1873 Meiji 7 = 1874 Meiji 8 = 1875 Meiji 9 = 1876 Meiji 10 = 1877. The last part of this article series about the role of art prints during the Japanese Meiji era () is a wrapup of the major differences in political and social aspects of the Japanese art print in Edo and Meiji era.
The Meiji era (明治, Meiji, Japanese pronunciation meꜜː(d)ʑi) is an era of Japanese history which extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912 This era represents the first half of the Empire of Japan, during which period the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonisation by Western powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialised nation. The Meiji period or Meiji era extended from the 23rd of October 1868 to the 30th of July in 1912 This was the period that represented the first half of Japan’s empire The Japanese society shifted from being a remote feudal society to a Westernized form. These important changes occurred in the Meiji period Japan went through two periods of economic development First, the Tokugawa shogun was overthrown called the Prewar Japan Secondly, the Meiji government was founded and Japanese Westernization began This era was named Postwar Japan.
The Meiji Period is a term used to refer to the 45year reign of Emperor Meiji in Japan, from 1868 to 1912 The Meiji Period marked the end of the Tokugawa Shogunate and was a major shift in Japanese culture. () The reign of Emperor Meiji and the beginning of Japan's modern period It started on October 23, 1868, when the 16yearold emperor Mutsuhito selected the era name "Meiji" ("enlightened rule") for his reign;. 1415 (Meiji 2728) First SinoJapanese War;.
Prostitutes on display behind a cage in Yoshiwara, one of Tokyo's red light districts, circa 1910 (roughly six years before the practice, known as harimise, was stopped);. His imperial power was restored The actual political power was transferred from the Tokugawa Bakufu into the hands of a small group of nobles and former samurai. Meiji, in full Meiji Tennō, personal name Mutsuhito, (born Nov 3, 1852, Kyōto—died July 30, 1912, Tokyo), emperor of Japan from 1867 to 1912, during whose reign Japan was dramatically transformed from a feudal country into one of the great powers of the modern world.
There are 349 meiji era for sale on Etsy, and they cost $ on average The most common meiji era material is metal The most popular color?. ECONEMY Japan’s industrial revolution occurred during the Meiji era causing a major economic boom In 1868, Japan emerged as the first industrialised Asian nation The Meiji rulers used a market economy and followed British and North American examples of free enterprise capitalism. The motto of the era was “Enrich the Country and Strengthen the Military” and at the helm of this effort was Emperor Meiji He embraced these efforts both in practice and in appearance He wore Westernstyle military clothing, styled his hair in a Western manner, and grew a kaiser mustache.
Most of the change occurred during the Meiji period which began in 1868 and lasted until 1912 Lots of things were modified in during this time Here are some examples Education was a main social system that changed during modernization In the Edo period, school was only for children of people in higher classes. The Meiji era (明治, Meiji, Japanese pronunciation meꜜː(d)ʑi) is an era of Japanese history which extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912 This era represents the first half of the Empire of Japan, during which period the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonisation by European powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialised nation. Following the death of his father in.
The Meiji period, which ran from 1868 to 1912, marks one of the key turning points in both Japanese architecture and the history of the country as a whole The almost 300yearlong Edo era ended abruptly in 1868 when Emperor Meiji took over in a bid to bring Japan up to speed with the Western world. Japanese women during the Meiji Restoration (left to right) a painting depicting Meiji era women at work;. Woodblock Prints from the Meiji Era All prints on display are from our archive of sold Japanese prints Chikanobu Toyohara Item # Title Ueno Exposition Sold $170 1/9/05 Ueno Exposition Chikanobu Toyohara Item # Title Meiji Emperor and Empress Sold $240 8/27/06.
The Reign of the Meiji Emperor When the Meiji emperor was restored as head of Japan in 1868, the nation was a militarily weak country, was primarily agricultural, and had little technological development It was controlled by hundreds of semiindependent feudal lords. E Meiji period (明治時代, Meijijidai), also known as the Meiji era, was a Japanese era name (年号,, nengō,, lit "year name") after Keiō and before Taishō This period started in September 1868 and ended in July 1912 During this time, the emperor was Meiji tennō (明治天皇). The period before the Meiji era was known as the Edo era (), when Japan was ruled as a collection of fiefdoms under the Tokugawa shogunate, a military dictatorship that was based in Edo.
Meiji Restoration (Meijiishin) The Meiji Restoration was the historic change from the feudal system of the Edo Shogunate to the system of direct Imperial rule by the Meiji government through the overthrow of the Shogunate, and the accompanying series of wars (the Boshin War) and reforms. (Meiji 3738) RussoJapanese War;. Change was the currency of the Meiji era (1868–1912) From the day the teenaged Mutsuhito claimed power on January 3, 1868 in a relatively tranquil coup called the “Meiji Restoration” (after his reign name) until his death fortyfive years later, Japan experienced an evolution so rapid that one Tokyo expatriate said he felt as if he had.
The Meiji era (which means “enlightened rule”) was officially established on Oct 23 Fighting, however, continued into 1869 and beyond, and the imperialists also abandoned their goal of expelling. The Japanese Meiji period, defined as the period between 1868 and 1912, was an era in which artists were forced to respond to these questions on a new scale Meiji Japan was famously the era in which, after nearly 300 years of almost complete isolation from the globe, Japan began to trade openly with Europe and the West. Era name changed to Meiji 1869 New government wins total control of Japan as Boshin Civil War ends Domains return territory and citizens to the state 1871 Domains replaced by prefectures.
Introduction The start of the Meiji Era and the beginning of Japan’s road to modernization, started when the 16 year old emperor Mutsuhito selected the era name Meiji for his reign This period commenced with the collapse of the Tokugawa Shogunate and led to Japan’s transformation from a feudal nation into a modern industrial state. Satsuma Pottery from the Meiji Period is a popular choice among collectors and antique buyers due to the historic times when it was created as well as the fine craftsmanship and quality The style of painting on many pieces from the Meiji period is known as Kinrande or "gild on". Japan’s industrial revolution occurred during the Meiji era causing a major economic boom In 1868, Japan emerged as the first industrialised Asian nation The Meiji rulers used a market economy and followed British and North American examples of free enterprise capitalism One of the first changes to be made was the currency.
Mikao Usui in the MeijiEra () The following article describes the historical context of Mikao Usui () life and the Meiji period () The Meiji period is a period in Japanese history, which includes much of the life of Mikao Usui It begins with the enthronement of Emperor Mutsuhito () in 1868 At that time. The Japanese Meiji period, defined as the period between 1868 and 1912, was an era in which artists were forced to respond to these questions on a new scale Meiji Japan was famously the era in which, after nearly 300 years of almost complete isolation from the globe, Japan began to trade openly with Europe and the West. The Meiji Period is a term used to refer to the 45year reign of Emperor Meiji in Japan, from 1868 to 1912 The Meiji Period marked the end of the Tokugawa Shogunate and was a major shift in Japanese culture.
The capital of Japan moved from Kyoto to Tokyo;. The Meiji Period is the time of Japanese history between 1868 and 1912 It received its name from Emperor Meiji and was an era of innovation and opening to Western influences. 1810 (Meiji 2223) Constitution of the Empire of Japan;.
Meiji Period (1868 1912) In 1867/68, the Tokugawa era found an end in the Meiji Restoration The emperor Meiji was moved from Kyoto to Tokyo which became the new capital;. Meiji, in full Meiji Tennō, personal name Mutsuhito, (born Nov 3, 1852, Kyōto—died July 30, 1912, Tokyo), emperor of Japan from 1867 to 1912, during whose reign Japan was dramatically transformed from a feudal country into one of the great powers of the modern world The second son of the emperor Kōmei, Mutsuhito was declared crown prince in 1860;. The emperor himself is therefore posthumously known as Meiji The period commenced with the collapse of the Tokugawa Shogunate and the sweeping reforms.
Japanese Art of the Meiji Period (1868 – 1912) The Khalili Collection of Japanese Art, the world’s most comprehensive collection of Meiji decorative art, comprises over 1,600 pieces including works by most of the known masters from the middle of the 19th century to the early th century. Sep 27, 14 Explore Mary Thompson's board "Meiji Era", followed by 372 people on See more ideas about Meiji era, Japanese art, Japanese. The emperor himself is therefore posthumously known as Meiji.
Japan’s industrial revolution occurred during the Meiji era causing a major economic boom In 1868, Japan emerged as the first industrialised Asian nation The Meiji rulers used a market economy and followed British and North American examples of free enterprise capitalism One of the first changes to be made was the currency. The Meiji era (明治, Meiji, Japanese pronunciation meꜜː(d)ʑi) is an era of Japanese history which extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912 This era represents the first half of the Empire of Japan, during which period the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonisation by European powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialised nation. Meiji Restoration, in Japanese history, the political revolution in 1868 that brought about the final demise of the Tokugawa shogunate (military government)—thus ending the Edo (Tokugawa) period (1603–1867)—and, at least nominally, returned control of the country to direct imperial rule under Mutsuhito (the emperor Meiji).
30 July 1912 (Meiji 45, 30th day of the. The Meiji period ( 明治時代, Meijijidai ), also known as the Meiji era, is a Japanese era which extended from October 23, 1868, to July 30, 1912 7 The Meiji period saw a flowering of public discourse on the direction of Japan. Yoshiwara prostitutes in a brothel;.
Japanese women at work in a. Japan’s Tokugawa (or Edo) period, which lasted from 1603 to 1867, would be the final era of traditional Japanese government, culture and society before the Meiji Restoration of 1868 toppled the. The Meiji Era was the 44year period of Japan's history from 1868 to 1912 when the country was under the rule of the great Emperor Mutsuhito Also called the Meiji Emperor, he was the first ruler of Japan to wield actual political power in centuries An Era of Change.
The Meiji period, which ran from 1868 to 1912, marks one of the key turning points in both Japanese architecture and the history of the country as a whole The almost 300yearlong Edo era ended abruptly in 1868 when Emperor Meiji took over in a bid to bring Japan up to speed with the Western world. Add year/month/day the era began 1867 to a date in Meiji 1911 to a date in Taisho 1925 to a date in Showa 19 to a date in Heisei. () The reign of Emperor Meiji and the beginning of Japan's modern period It started on October 23, 1868, when the 16yearold emperor Mutsuhito selected the era name "Meiji" ("enlightened rule") for his reign;.
After the first twenty years of the Meiji period, the industrial economy expanded rapidly until about 19 with inputs of advanced Western technology and large private investments Stimulated by wars and through cautious economic planning, Japan emerged from World War I as a major industrial nation* Meiji Era Industrialization Recognized by UNESCO.

Kunsthistorisches Museum Wien B2b Tourism Japan In The Meiji Era
Young Samurai Of The Meiji Era Between 1870 80 Colorization

Tradition And Innovation In Meiji Period Prints Risd Museum
Meiji Era のギャラリー

Visiting Tokyo In The Footsteps Of Emperor Meiji

Meiji Restoration Definition History Facts Britannica

Photography Japanese Meiji Era Aurora Club Tourist Photo Stewarts Military Antiques 00

Meiji Period In Japan Facing History And Ourselves

Japan In The Meiji Era Wall Street International Magazine

The Meiji Era 1868 1912 Japan Experience

The Meiji Restoration In Japan Japan City Tour

Looking At The Meiji Era Lily Absinthe
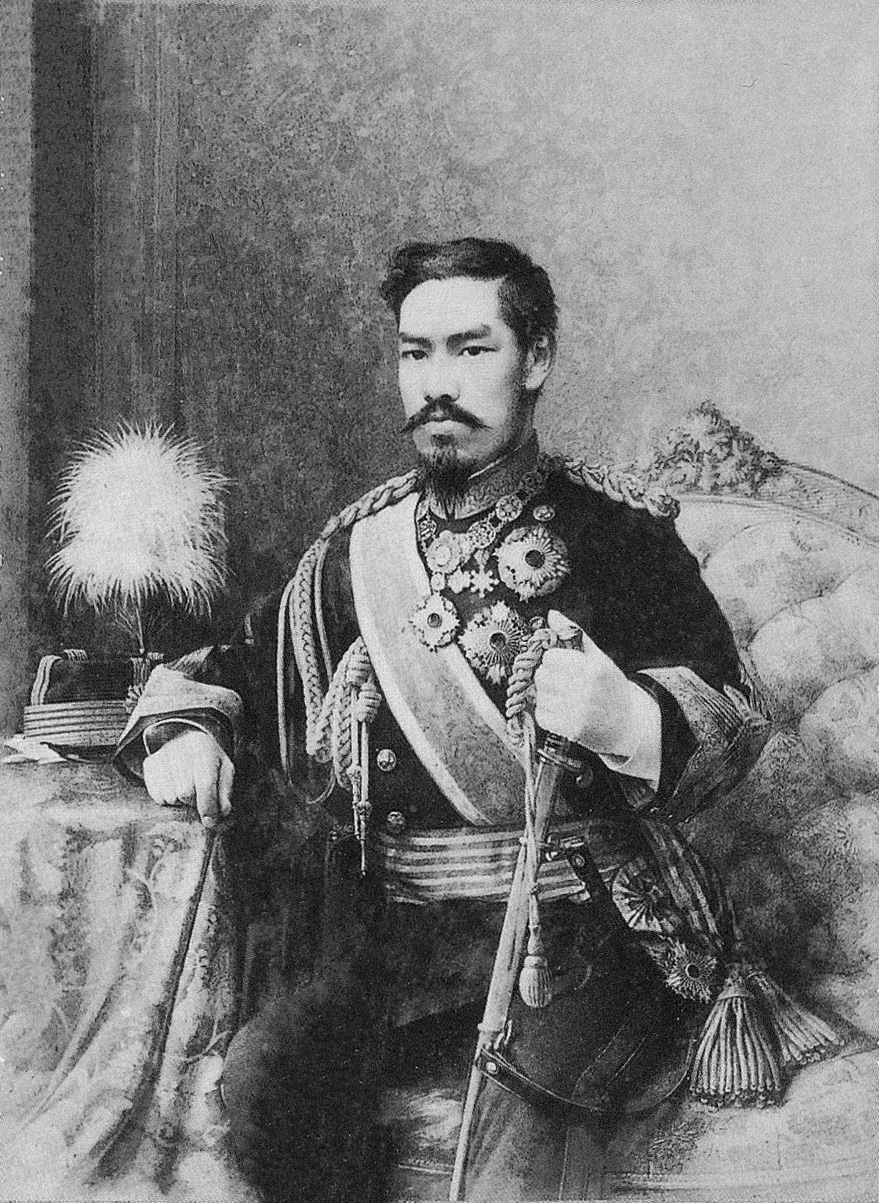

Emperor Meiji Wikipedia

Art Of Modernisation Meiji Era Woodblock Prints Insidejapan Tours

Biographies Of The People Involved In The Bakumatsu Meiji Era Tsunagu Japan

Meiji Era And Clothing

Women And Public Life In Early Meiji Japan

Meiji And Taishō Japan An Introductory Essay Tea Online Curriculum Projects University Of Colorado Boulder

Geisha Performance Meiji Era Japanese Woodblock Print

The Meiji Period Also Known As The Meiji Era Is A Japanese Era Which Extended From September 8 1868 Through July 30 1912 This Period Represents The First Half Of The Empire

Secrets Unravel During Repairs To Meiji Era Gown Worn By Empress The Asahi Shimbun

Meiji Era Japanese Woodblock Printing Taisho Era Japan

Meiji Period Japan History Japanvisitor Japan Travel Guide

When Art Met Craft In Meiji Era Japan The Japan Times

Meiji Period Artelino Ukiyoe Japan Illustration Japanese Prints

Meiji Era And Clothing

Female Samurai C Late 1800s Meiji Era Imgur

Embroidered Wonders Meiji Era Textiles In The Khalili Collections

Japanese Bathers Meiji Era Let S Get Lost

Tomioka Silk Mill Ranks As Meiji Era Industrial Gem The Japan Times

Becoming Modern Becoming Global Japanese Prints From The Meiji Period 1868 1912 Princeton University Art Museum

New Ace Attorney Set In Meiji Era News Nintendo World Report

The Meiji Period Also Known As The Meiji Era Is A Japanese Era Which Extended From September 8 1868 Through July 30 1912 This Period Represents The First Half Of The Empire

Meiji Period Artelino

Meiji Era Clothing High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy

Meiji Period 1868 1912 Reforms Modernization And Culture Facts And Details

Colorized Photo Of Maikos In The Meiji Era Japan 1868 1912 1577 X 1019 Historyporn

Fuji Arts Japanese Prints Original Meiji Era Kuchi E Print By Meiji Era Artist Not Read

Meiji Period Artelino

Fuji Arts Japanese Prints A Clearance Opportunity Meiji Or Edo Era Original By Meiji Era Artist Unsigned

Japan Awakens Woodblock Prints Of The Meiji Period

Manga Tells How A British Women Travelled Through Japan In Meiji Era Culture Tokyo Business Today All The News You Need To Know About Japan

Japan At The Dawn Of The Modern Age Woodblock Prints From The Meiji Era Keene Donald Morse Anne Nishimura Sharf Frederic Virgin Louise Sharf Frederic A Amazon Com Books

The Meiji Era 1868 1912 Japan Experience

The Meiji Era 1868 1912 Japan Experience

About Japan A Teacher S Resource The Meiji Restoration Era 1868 18 Japan Society

Meiji Era Wikipedia

4qx04g60elqibm

Japanese Imperial Family Meiji Era Vintage Beauty Beautyvintage Vintagebeauty Japan Vintagejapan Starinnye Fotografii Starye Fotografii Vintazhnye Foto

Looking At The Meiji Era Lily Absinthe

Women In Meiji Japan Exploring The Underclass Of Japanese Industrialization Inquiries Journal

Portrait Of Three People Of Meiji Era Japan Nippon Graph Meiji Era Portrait Japan Photo

Behind The Revisions Of The Unequal Treaties During The Meiji Period The University Of Tokyo

Meiji Restoration Wikipedia

Fuji Arts Japanese Prints Original Meiji Era Kuchi E Print By Meiji Era Artist Not Read

Meiji Period 1868 1912 Reforms Modernization And Culture Facts And Details

What To Know About The Meiji Era As Modern Japan Turns 150 Quartz

2 103 Meiji Period Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images

Exploring Antiques From The Meiji Period Patrick Moorhead Antiques

Japanese Meiji Period Military Uniforms Medal Photo Book Before Ww2 For Sale Online Ebay
File Yokohama Otamachi In The Meiji Era Jpg Wikimedia Commons

Meiji Ladies003 Japanese Woodblock Printing Japanese Prints Japan Art

Meiji Emperor And Empress Riding In A Carriage 10 By Meiji Era Artist Not Read Japanese Woodblock Printing Japanese Painting Japan Art

Tradition And Innovation In Meiji Period Prints Risd Museum

Meiji 150th The Origin Of Fundamental Values Of Japan Youtube

Column Nishiki E Brocade Pictures In The Meiji Era The Landmarks Of Edo In Color Woodblock Prints

136 The Tabloids Of Meiji Era Japan Inspired By The Frustrations Of Heath Houston By Betta Tryptophan Medium

The Japanese Body A Contested Terrain In The Meiji Restoration Era By Emilia Boulton The Rcdf

Meiji Period

Japanese Art In The Meiji Period

Today In History End Of The Meiji Era Interest Anime News Network
/Emperor_Meiji_Takahashi_Yuichi-5a0c972fec2f64003685cc36.jpg)
Japan S Meiji Era
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Emperor_Meiji_Takahashi_Yuichi-5a0c972fec2f64003685cc36.jpg)
Japan S Meiji Era

The Meiji Restoration Imperial Japan Japanistry Com

Meiji Period Youtube

Japan The Meiji Period September 1868 To July 1912

Imperial Exposures The Multiple Photographic Bodies Of Rulers In The Meiji Period Japan And Paris Paris And Japan
-to-meiji-era-(1868-1912),-comprising-two-oban-tate-e-triptychs-and-one-oban.jpg)
Edo Period 1615 1868 To Meiji Era 1868 1912 Comprising Two Oban Tate E Triptychs And One Oban Yoko E Print By Various Asian Artists On Artnet

Japanese Marriage Ceremony In The Late Meiji Era 1868 1912 Caption Stock Photo Alamy

Ginza Japan In The Meiji Restoration Fashion In Meiji Restoration

Meiji Restoration Definition History Facts Britannica

Meiji Period In Japan Facing History And Ourselves
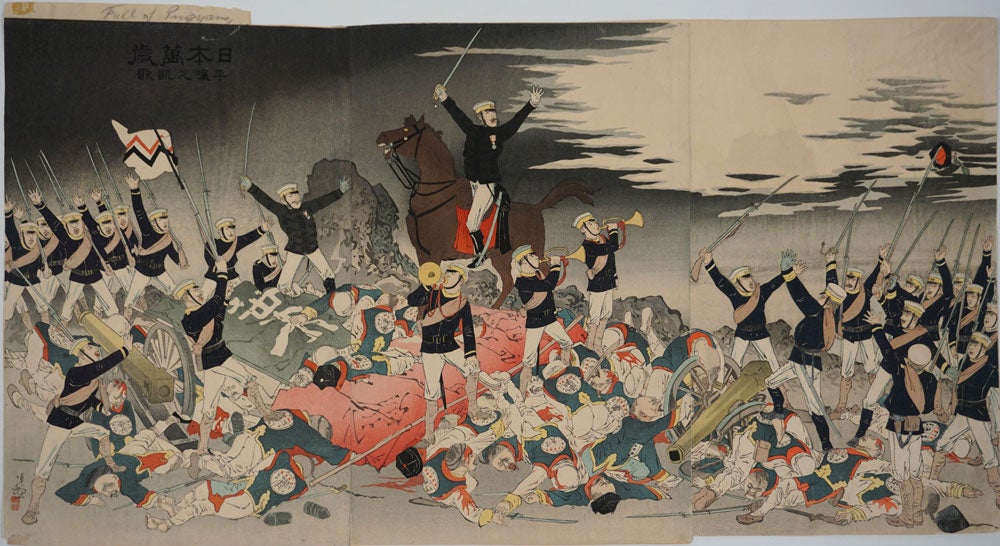

Hurrah For Japan The Victory Song Of Pyongyang Meiji Era Japanese Triptych Woodblock Kobayashi Kiyochika

Meiji Era And Japanese Prints Artelino

Letters From The Meiji Era Process

Meiji Era Wikipedia

New Japanese Banknotes To Feature International Minded Thinkers From The Meiji Era Nippon Com
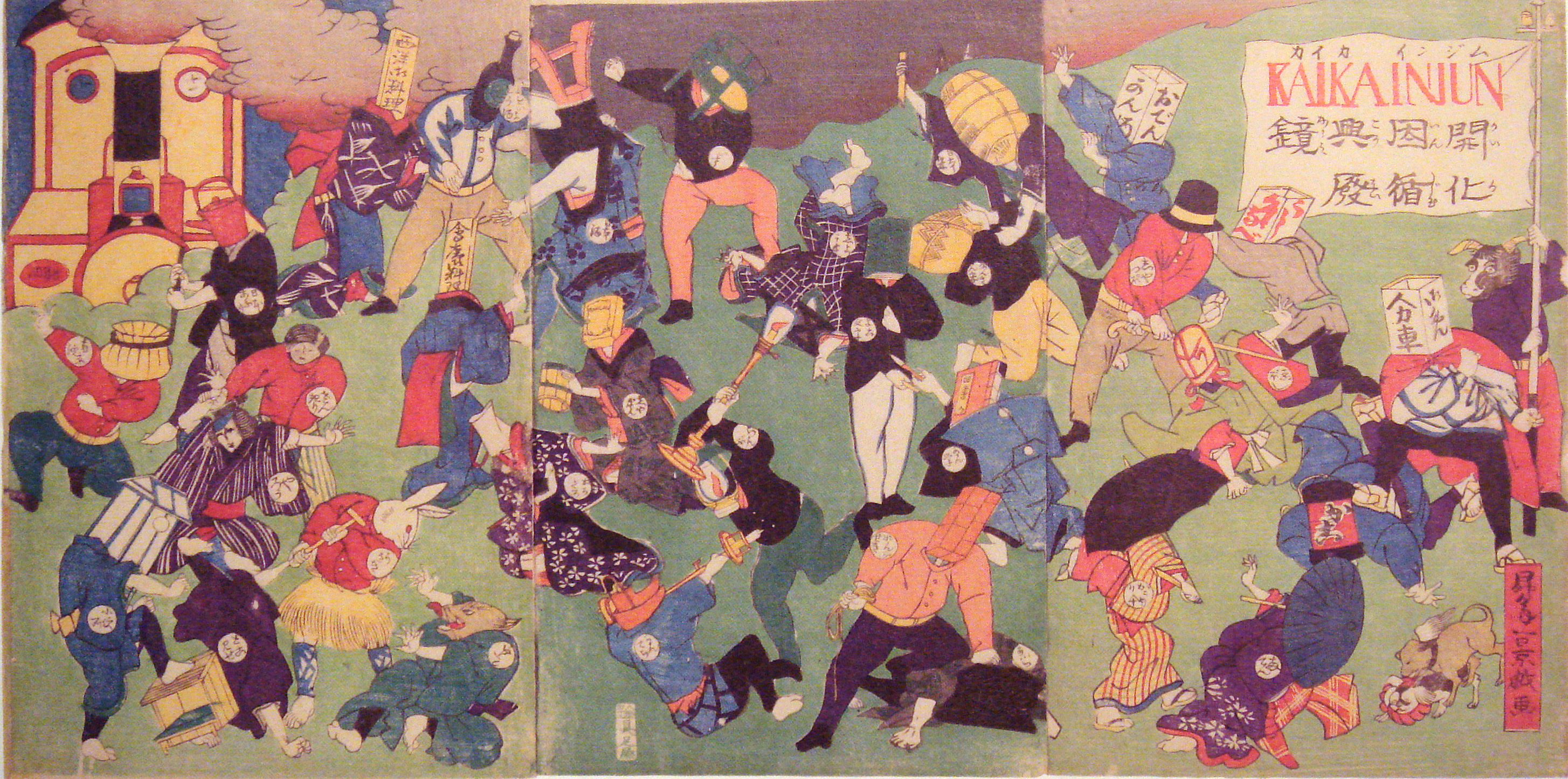

Meiji Restoration Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia

Meiji Period Artelino
Toshimasa Civil And Military Officers Japan Meiji Period 1868 1912 The Metropolitan Museum Of Art

Meiji Period Japan History Japanvisitor Japan Travel Guide
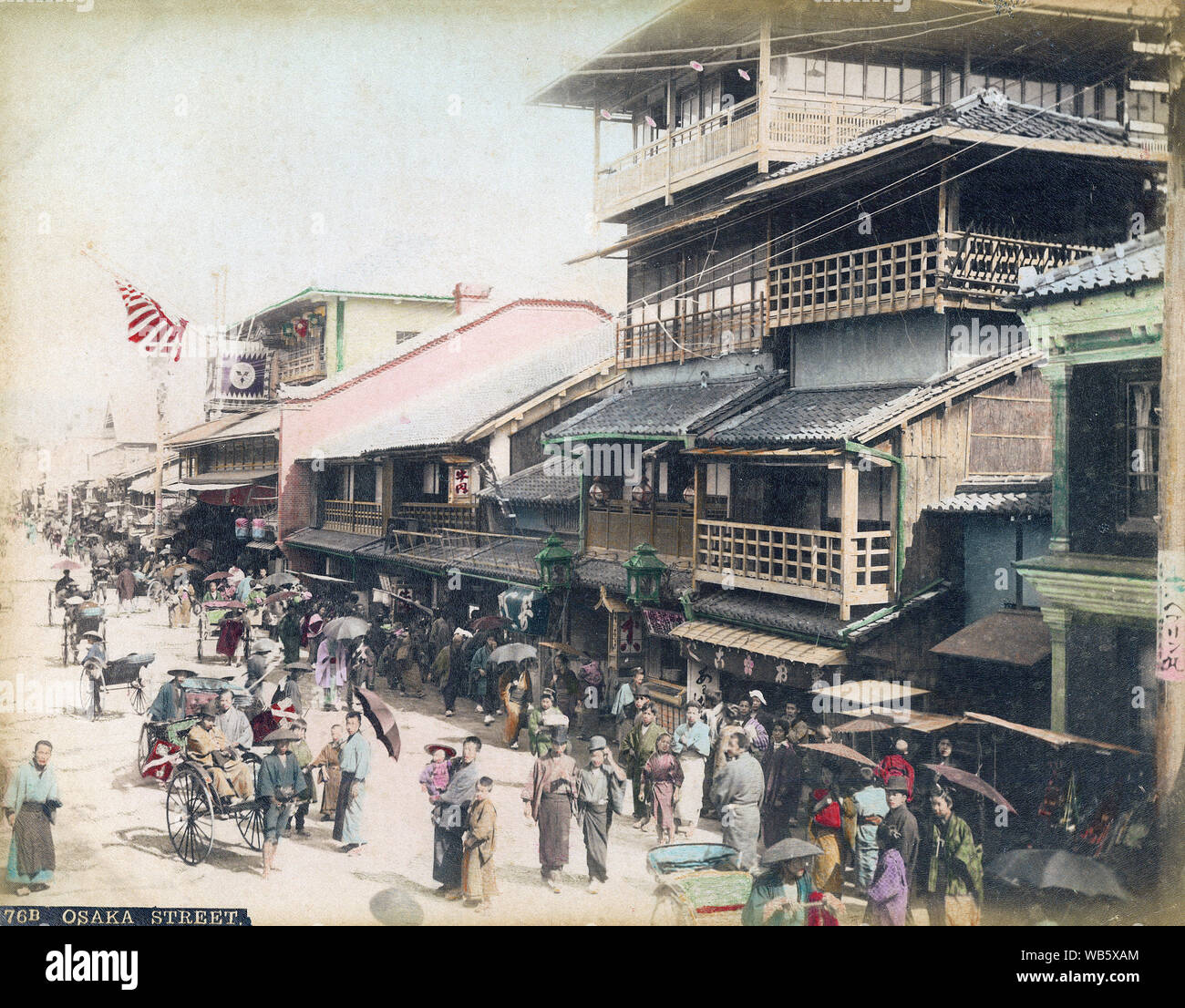

Page 2 Meiji Period High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
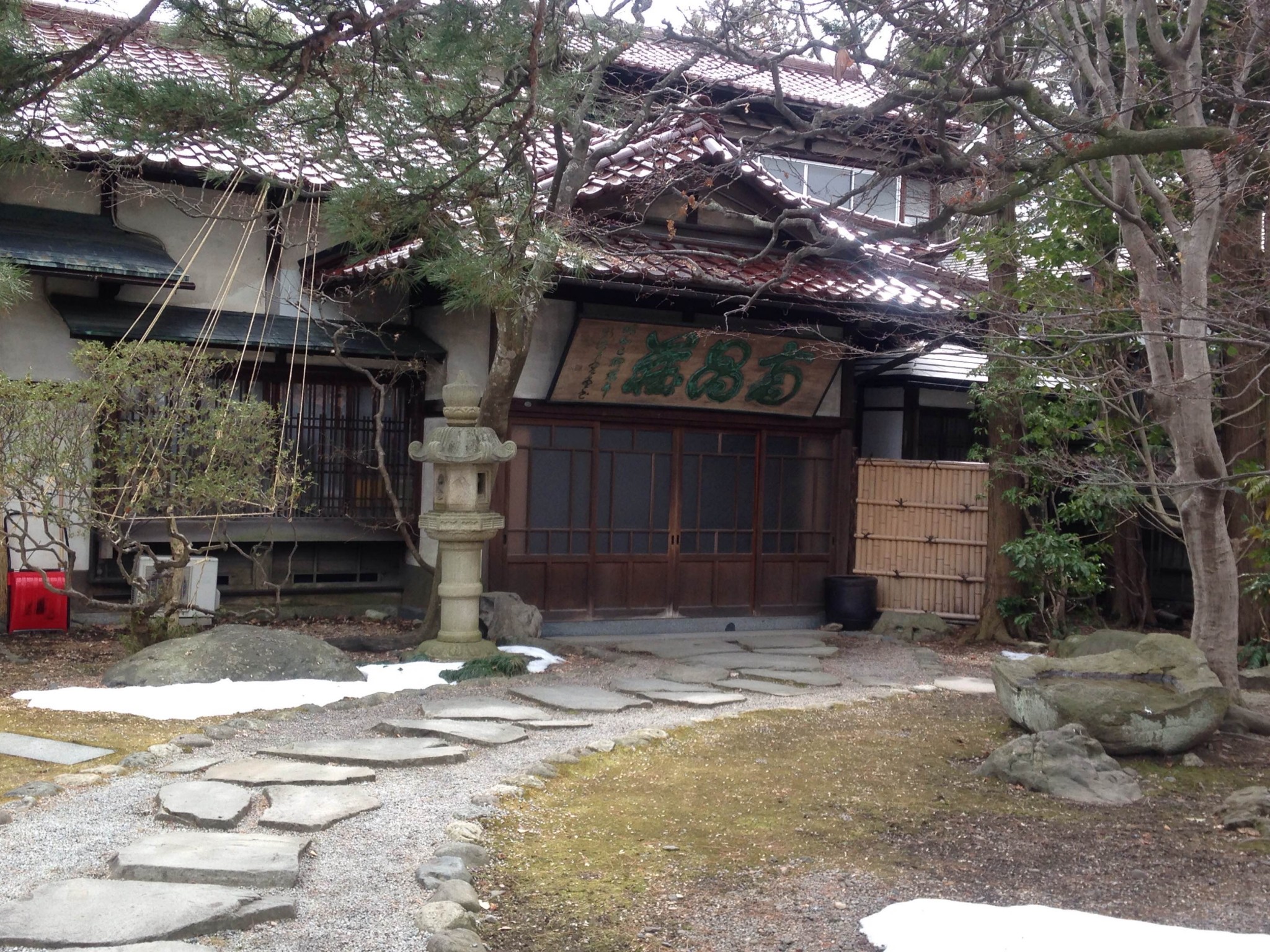

Nanshoso House A Remnant Of The Meiji Era

The Meiji Period Japanese Encyclopedia Matcha Japan Travel Web Magazine

Meiji Period Art Porcelain Architecture In Japan Study Com

The Meiji Era 1868 1912 Japan Experience
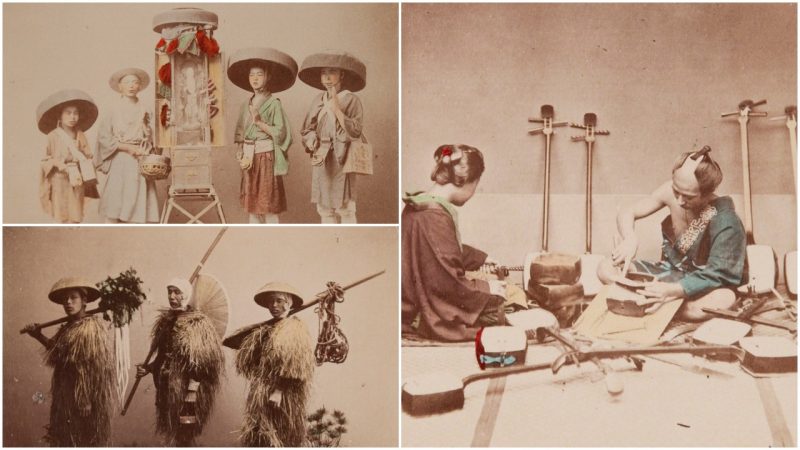

Hand Colored Photographs Capture Japanese Life During The Meiji Period

Japan At The Dawn Of The Modern Age Woodblock Prints From The Meiji Era By Donald Keene

Tokugawa Period And Meiji Restoration History

Meiji Period Japan History Japanvisitor Japan Travel Guide

File Shimoyokogai Dori Street At Tainan Under Meiji Era Jpg Wikimedia Commons



